Kalman Linear Attention: Parallel Bayesian Filtering For Efficient Language Modelling and State Tracking
11 Feb, 2026·, ,,,·
0 min read
,,,·
0 min read
Vaisakh Shaj
Cameron Barker
Aidan Scannell
Andras Szecsenyi
Elliot J. Crowley
Amos Storkey
Abstract
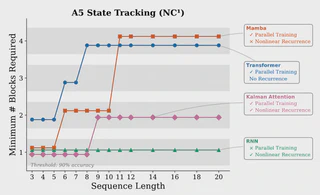
State-space language models such as Mamba and gated linear attention (GLA) offer efficient alternatives to transformers due to their linear complexity and parallel training, but often lack the expressivity and robust state-tracking needed for complex reasoning. We address these limitations by reframing sequence modelling through a probabilistic lens, using Bayesian filters as a core primitive. While classical filters such as Kalman filters provide principled state estimation and uncertainty tracking, they are typically viewed as inherently sequential. We show that reparameterising the Kalman filter in information form enables its updates to be computed via an associative scan, allowing efficient parallel training. Building on this insight, we introduce the Kalman Linear Attention (KLA) layer, a neural sequence-modelling primitive that performs time-parallel probabilistic inference while maintaining explicit belief-state uncertainty. KLA offers strictly more expressive nonlinear updates and gating than GLA variants while retaining their computational advantages. On language modelling tasks, KLA matches or outperforms modern SSMs and GLAs across representative discrete token manipulation and state-tracking benchmarks.
Type
Publication
arXiv preprint arXiv:2602.10743